West Bengal is situated in eastern India and shares its borders with Jharkhand, Bihar, Odisha, Sikkim and Assam. The State also shares international borders with Bangladesh, Bhutan and Nepal. The Bay of Bengal is at the south of the State.


 Location Advantage
Location Advantage
Its locational advantage makes the state a traditional market for eastern India, the Northeast, Nepal and Bhutan. It is also a strategic entry point for markets in Southeast Asia. The cost of operating a business is lower in Kolkata than in other metropolitan cities. The State has potential consumer base of 300 million people.
 4th Largest Economy
4th Largest Economy
West Bengal, India’s fourth largest economy, with a population of 91.3 million, had a gross state domestic product (GSDP) of Rs. 794938.62 crore in 2018-19. The state’s GSDP expanded at a CAGR of 9.15% during 2017-18.(source - Economic Review, 2018-19)
 Top Notch Institutes
Top Notch Institutes
There are 21 State-aided Universities, 6 State Specialised Universities, 1 Deemed University, 8 Central Universities and Institutes of Higher Learning, 10 Private universities and size-able research institutes in West Bengal. It is host to top-notch institutes like IIT Kharagpur, IIEST-Shibpur, NIT-Durgapur, Jadavpur University and Calcutta University. Knowledge of English is an advantage for the workforce of West Bengal, especially in Kolkata. (source - official website of Deptt. of Higher Education, GoWB)
 Top IT and ITeS Companies
Top IT and ITeS Companies
Over 500 IT and ITeS companies operate in the state, employing more than 120,000 professionals.The state government has started work on the 13 proposed IT parks,The IT parks will be located mostly in tier-II cities like Asansol, Kharagpur, Malda, Haldia, Durgapur, Kalyani, Rajarhat, Siliguri. The work for the IT park at Durgapur is in advanced stages.
 Rich in Natural Resources
Rich in Natural Resources
West Bengal has abundant natural resources of minerals and suitable agro-climatic conditions for agriculture, horticulture and fisheries. It is in the vicinity to mineral rich states like Jharkhand, Bihar and Odisha.
 Excellent Connectivity
Excellent Connectivity
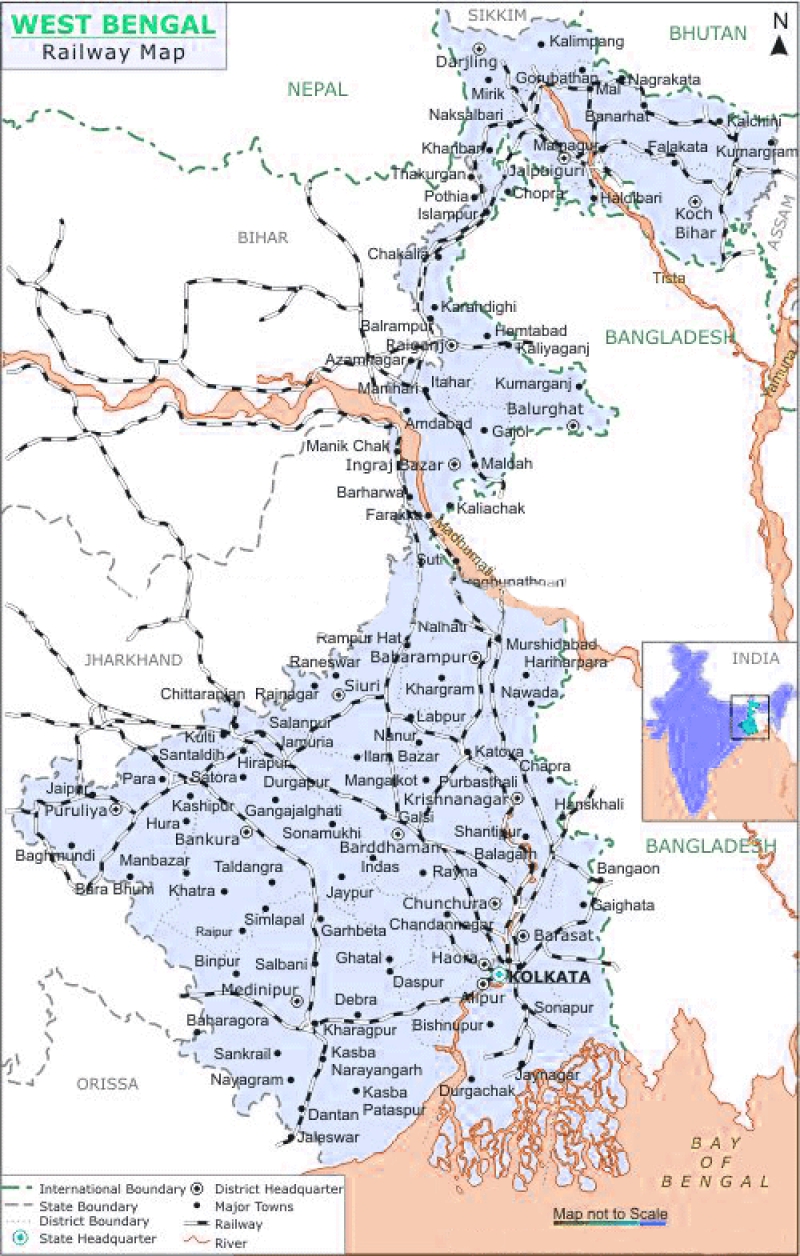
West Bengal offers excellent connectivity to the rest of India in terms of railways, roadways, ports and airports. Major stretches of the golden quadrilateral project also pass through the northern districts of the state.


 Location Advantage
Location Advantage
Its locational advantage makes the state a traditional market for eastern India, the Northeast, Nepal and Bhutan. It is also a strategic entry point for markets in Southeast Asia. The cost of operating a business is lower in Kolkata than in other metropolitan cities. The State has potential consumer base of 300 million people.
 4th Largest Economy
4th Largest Economy
West Bengal, India’s fourth largest economy, with a population of 91.3 million, had a gross state domestic product (GSDP) of Rs. 794938.62 crore in 2018-19. The state’s GSDP expanded at a CAGR of 9.15% during 2017-18.(source - Economic Review, 2018-19)
 Top Notch Institutes
Top Notch Institutes
There are 21 State-aided Universities, 6 State Specialised Universities, 1 Deemed University, 8 Central Universities and Institutes of Higher Learning, 10 Private universities and size-able research institutes in West Bengal. It is host to top-notch institutes like IIT Kharagpur, IIEST-Shibpur, NIT-Durgapur, Jadavpur University and Calcutta University. Knowledge of English is an advantage for the workforce of West Bengal, especially in Kolkata. (source - official website of Deptt. of Higher Education, GoWB)
 Top IT and ITeS Companies
Top IT and ITeS Companies
Over 500 IT and ITeS companies operate in the state, employing more than 120,000 professionals.The state government has started work on the 13 proposed IT parks,The IT parks will be located mostly in tier-II cities like Asansol, Kharagpur, Malda, Haldia, Durgapur, Kalyani, Rajarhat, Siliguri. The work for the IT park at Durgapur is in advanced stages.
 Rich in Natural Resources
Rich in Natural Resources
West Bengal has abundant natural resources of minerals and suitable agro-climatic conditions for agriculture, horticulture and fisheries. It is in the vicinity to mineral rich states like Jharkhand, Bihar and Odisha.
 Excellent Connectivity
Excellent Connectivity
West Bengal offers excellent connectivity to the rest of India in terms of railways, roadways, ports and airports. Major stretches of the golden quadrilateral project also pass through the northern districts of the state.


Till date WBIIDC has established 18 (Eighteen) lndustrial Growth Centres on Build, Operate & Maintain basis. These are geographically spread across West Bengal catering to needs of both advanced & backward industrial regions of the state.
All supporting infrastructure relating to Roads, Drainage, Water Supply, Power Supply, Street Lighting, Common Facilities Centre etc. have been developed by WBIIDC. Administrative Offices with supporting infrastructure & maintenance service exist for all such centres. Lands / Sheds have been allotted to various industrial units on 99 years lease.
Prominent Investors in Industrial Growth Centres



Till date WBIIDC has established 18 (Eighteen) lndustrial Growth Centres on Build, Operate & Maintain basis. These are geographically spread across West Bengal catering to needs of both advanced & backward industrial regions of the state.
All supporting infrastructure relating to Roads, Drainage, Water Supply, Power Supply, Street Lighting, Common Facilities Centre etc. have been developed by WBIIDC. Administrative Offices with supporting infrastructure & maintenance service exist for all such centres. Lands / Sheds have been allotted to various industrial units on 99 years lease.
Prominent Investors in Industrial Growth Centres

The ancilliary State agencies engaged in production, transmission and distribution are:
Transmission in West Bengal: WBSETCL
| Total No. of EHV Sub-Station | 128 nos. |
|---|---|
| Total EHV Lines | 13935 CKM |
| Amount of energy handled per year ( in MU ) |
|
| Achievement of the individual Entities to be highlighted |
|





Allotment of Land & Module since 2011-12 upto 2019-20
Land based Industrial Parks
| Year | Area (in acre) | Proposed Investment (Rs. Crore) | Proposed Employment (D + I) | No. of Units |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2011-12 | 618.34 | 7551.38 | 13490 | 10 |
| 2012-13 | 30.13 | 621.39 | 4751 | 6 |
| 2013-14 | 295 | 1428.14 | 3326 | 4 |
| 2014-15 | 33.81 | 323.13 | 1267 | 11 |
| 2015-16 | 115.241 | 1220.46 | 2781 | 8 |
| 2016-17 | 22.13 | 170.89 | 538 | 7 |
| 2017-18 | 81.19 | 336.28 | 1542 | 7 |
| 2018-19 | 229.43 | 1891.15 | 20899 | 14 |
| 2019-20 | 21.22 | 96.69 | 916 | 4 |
| Total | 1446.491 | 13639.51 | 49510 | 71 |
Module based Industrial Parks
| Year | Area (in acre) | Proposed Investment (Rs. Crore) | Proposed Employment (D + I) | No. of Units |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2011-12 | 56080 | 23.12 | 517 | 4 |
| 2012-13 | 33648 | 19.84 | 320 | 4 |
| 2013-14 | 61085.4 | 41.65 | 883 | 4 |
| 2014-15 | 146961.58 | 109.49 | 2346 | 29 |
| 2016-17 | 1080.63 | 0.93 | 8 | 1 |
| 2018-19 | 35732.54 | 18.53 | 434 | 3 |
| 2019-20 | 10129.87 | 6.15 | 549 | 4 |
| Total | 387430.28 | 241.77 | 5581 | 59 |
The ancilliary State agencies engaged in production, transmission and distribution are:
Transmission in West Bengal: WBSETCL
| Total No. of EHV Sub-Station | 128 nos. |
|---|---|
| Total EHV Lines | 13935 CKM |
| Amount of energy handled per year ( in MU ) |
|
| Achievement of the individual Entities to be highlighted |
|




Allotment of Land & Module since 2011-12 upto 2019-20
Land based Industrial Parks:
| Year | Area (in acre) | Proposed Investment (Rs. Crore) | Proposed Employment (D + I) | No. of Units |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2011-12 | 618.34 | 7551.38 | 13490 | 10 |
| 2012-13 | 30.13 | 621.39 | 4751 | 6 |
| 2013-14 | 295 | 1428.14 | 3326 | 4 |
| 2014-15 | 33.81 | 323.13 | 1267 | 11 |
| 2015-16 | 115.241 | 1220.46 | 2781 | 8 |
| 2016-17 | 22.13 | 170.89 | 538 | 7 |
| 2017-18 | 81.19 | 336.28 | 1542 | 7 |
| 2018-19 | 229.43 | 1891.15 | 20899 | 14 |
| 2019-20 | 21.22 | 96.69 | 916 | 4 |
| Total | 1446.491 | 13639.51 | 49510 | 71 |
Module based Industrial Parks:
| Year | Area (in acre) | Proposed Investment (Rs. Crore) | Proposed Employment (D + I) | No. of Units |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2011-12 | 56080 | 23.12 | 517 | 4 |
| 2012-13 | 33648 | 19.84 | 320 | 4 |
| 2013-14 | 61085.4 | 41.65 | 883 | 4 |
| 2014-15 | 146961.58 | 109.49 | 2346 | 29 |
| 2016-17 | 1080.63 | 0.93 | 8 | 1 |
| 2018-19 | 35732.54 | 18.53 | 434 | 3 |
| 2019-20 | 10129.87 | 6.15 | 549 | 4 |
| Total | 387430.28 | 241.77 | 5581 | 59 |